Overview
LH2CRAFT is a 4-year Research & Innovation project, being funded by the Clean Hydrogen Joint Undertaking of the EU and the UK Research & Innovation (UKRI) for the UK-based partners as well as receiving contributions from the private sector (grant-numbers 10082044 and 10070575). The project was the only proposal that was awarded by the EU within the Call for Proposals (HORIZON-JTI-CLEANH2-2022-02-06: ‘Development of large scale LH2 containment for shipping.’).
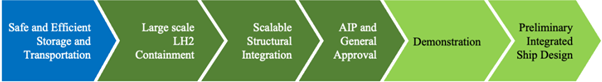
The overall goal of LH2CRAFT is to develop a next generation sustainable, commercially attractive, and safe technology for long-term storage and long-distance transportation of Liquid Hydrogen (LH2) on ships; to be realised by developing new design solutions for storage at a temperature of 20 K and demonstrating it on a 180 m3 containment system. Two societal objectives will be served: society’s needs and EU’s strong global maritime leadership with major impacts on EU’s innovation-driven industry providing highly skilled jobs, efficient technological solutions, and international regulatory standards.